 5 min.
read
5 min.
read
Digital technologies have grown exponentially and their use has become globalized. Continuous connectivity reaches a large part of humanity thanks to the widespread use of smartphones. Also, to the consequent access to information, social networks and audiovisual entertainment. However, the connectivity in Latin America has not allowed companies to make progress towards their digital transformation (CEPAL, 2021).
According to the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB, 2020), the delay in connectivity in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) has dramatically aggravated the economic and social consequences of the pandemic. The imposed confinement increased the demand for digital tools that allow remote continuity of activities. However, the lack of connectivity in countries hinders the acceleration of digital transformation.
Learn about the 5 reasons why the connectivity in Latin America has delayed the digital transformation of companies.
5 reason that have delayed companies digital transformation
1. Limitations of connectivity offer in Latin America
During the pandemic, broadband networks increased and covered great part of the population. However, there are differences within countries due to supply constraints of connectivity in Latin America.
Connectivity in rural areas is significantly lower than in urban areas, with the exception of Brazil, where the gap between connectivity by area is smaller, 66% urban vs 41% rural (OECD). In Mexico, for example, only 20% of the territory has Internet connection and rural areas have less coverage. 5.4% of the rural population has a connection, while in urban areas they have 78.3% coverage. (INEGI 2021)
In Peru, urban areas have 38% connectivity, while rural areas only have 2%. The same is true in other countries such as El Salvador and Bolivia (IDB, 2020).
2. Connection quality .
.
It is also important to consider the quality of the connection, estimated by the download speed. This is key to efficiently carry out productive activities remotely. Social distance measures forced to perform various tasks from the household, often simultaneously (ECLAC, 2021).
In September 2020, only six countries (Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize) had average download speeds on mobile broadband. This is the most used: greater than 25 megabits per second (Mbps). In addition, it is considered sufficient to develop several tasks of high data consumption simultaneously with the same connection (ECLAC, 2021).
Low speeds connectivity in Latin America led to exclusion in many cases, putting companies and their employees at a disadvantage. They cannot opt for their digital transformation for telework and online education solutions (CEPAL, 2021).
3. Diversity in countries
The difficulties faced by the region during the pandemic are linked to the economic diversity of LAC countries. It is about the difficulty on the part of the population to access information, knowledge or education through ICT. The lack of infrastructure and the connection quality are the main impediments to an efficient connectivity in Latin America (IDB, 2020).
Latin American networks have been affected by the exponential increase in traffic. In March 2020, Ecuador and Chile recorded a fixed broadband speed decline of 19.6% and 3%, respectively. And in Mexico, Brazil, Chile and Ecuador, an increase in suspension of 7.4%, 11.7%, 19% and 11.8% (CAF, 2020).
4. Digital gap between households and businesses
Digitalization of Latin American households indicates a growing connectivity and use of the Internet. This was projected at 78.78% during 2020, although it was lower in countries such as El Salvador with 45.02%, Honduras with 39.33% and Bolivia with 58.34%. Furthermore, rural/urban segmentation indicates an important level of digital marginalization (CAF, 2020).
This indicates that the connectivity in Latin America represents an obstacle to be overcome for important sectors of the population. Especially, in households that are more likely to leave the face-to-face transactions to move to digital ones.
Mainly, those who depended on Internet access to receive health information and educational content, do paperwork, or acquire goods electronically (CAF, 2020). *
As for businesses, Internet access in all countries can reach more than 85%. While for those who purchase inputs online, the percentage ranges from 15.20% in Peru to 66% in Brazil (CAF, 2020).
|
The usage percentage in electronic banking varies between 34.20% in Peru and 95.39% in Colombia |
Deficiencies are aggravated when weaknesses in the digital transformation of companies are analyzed. Specially, in the low digitalized areas such as interorganizational communication or the digitalization of land transport. This is an important weakness in dealing with the disruptions caused by the pandemic (CAF, 2020).
5.Limitations on demand: service costs
Limitations on demand for connectivity in Latin America focus on people who don't use the Internet. Access to broadband services is expensive in most LAC countries.
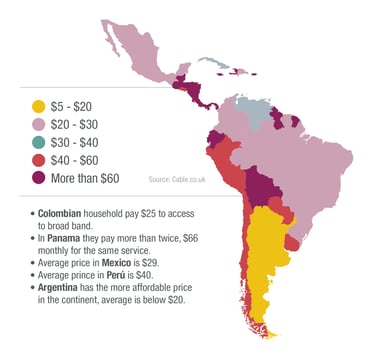 In 2018, the Broadband Commission for Sustainable Development set a target by 2025 to ensure that basic broadband services are affordable with costs corresponding to less than 2% of GDP per capita. During 2020, only Brazil and Costa Rica reached this goal, although several countries are very close to achieving it (IDB, 2020).
In 2018, the Broadband Commission for Sustainable Development set a target by 2025 to ensure that basic broadband services are affordable with costs corresponding to less than 2% of GDP per capita. During 2020, only Brazil and Costa Rica reached this goal, although several countries are very close to achieving it (IDB, 2020).
Mobile networks have met the demand for connectivity in Latin America in the low-income sector by making costs a little more accessible. However, basic access packages are limited to a monthly consumption of 1.5 GB. This makes their usefulness for work or study limited. Low levels of income in LAC households limit access to the Internet. And, therefore, the possibility of its efficient use (IDB, 2020).
This has consequences for the connectivity in Latin America both medium and long term. It creates a barrier to digitizing companies and other sectors of the economy. In addition, it increases economic and social inequality in the region (IDB, 2020).
Forecast of the evolution of connectivity in Latin AmericaDespite all these reasons, there is a forecast of evolution of the connectivity in Latin America. This focuses on the deployment of 5G networks.
The fifth generation of mobile networks will be disruptive for companies due to their technical characteristics (ECLAC, 2021):
Higher transmission speeds (up to 20 Gbps) and ultra-reliable low latency (less than one millisecond).
- Increased network security, massive machine-to-machine communications, and energy efficiency of devices.
- Better real-time access to information for decision making along the value chain. This ensures efficient use of resources and better response to demand.
The deployment of these networks will expand the connectivity in Latin America with wireless broadband services beyond mobile Internet. It targets complex Internet of Things systems, with low latency and high reliability. These are necessary to support critical applications in all economic sectors. In addition, they will allow innovative uses in virtually all industries based on the offer of improved experiences in broadband connectivity (ECLAC, 2021).
The efforts of Latin American banks to make progress in their digital transformation are also challenged by the reality of the connectivity in their countries. Both supply constraints and lack of infrastructure and connection quality for efficient connectivity. It is expected that demand will increase as the ratio of price and income is more appropriate, so a large market is still to be incorporated into digital banking for which we must be prepared.

Would you like to learn about our solutions, to develop your app as the gateway to your bank? This is a privileged gateway for digital onboarding.
Bibliographic references
- Inter-American Development Bank [IDB]. (2020). The impact of digital infrastructure on the consequences of COVID-19 and the mitigation of future effects. https://publications.iadb.org/publications/spanish/document/El-impacto-de-la-infraestructura-digital-en-las-consecuencias-de-la-COVID-19-y-en-la-mitigacion-de-efectos-futuros.pdf
- Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean [ECLAC]. (2021). Digital technologies for a new future. https://repositorio.cepal.org/bitstream/handle/11362/46816/1/S2000961_es.pdf
- Corporación Andina de Fomento [CAF]. (2020). The state of digitalization in Latin America in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic. https://scioteca.caf.com/bitstream/handle/123456789/1540/El_estado_de_la_digitalizacion_de_America_Latina_frente_a_la_pandemia_del_COVID-19.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- Corporación Andina de Fomento [CAF]. (2020). The opportunities of digitalization in Latin America in the face of Covid-19. https://scioteca.caf.com/bitstream/handle/123456789/1540/El_estado_de_la_digitalizacion_de_America_Latina_frente_a_la_pandemia_del_COVID-19.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- Pasquali, M. (2021, January 21). In which Latin American countries is internet more expensive? Statista. https://es.statista.com/grafico/23990/precio-de-internet-de-banda-ancha-fija-en-latinoamerica/



